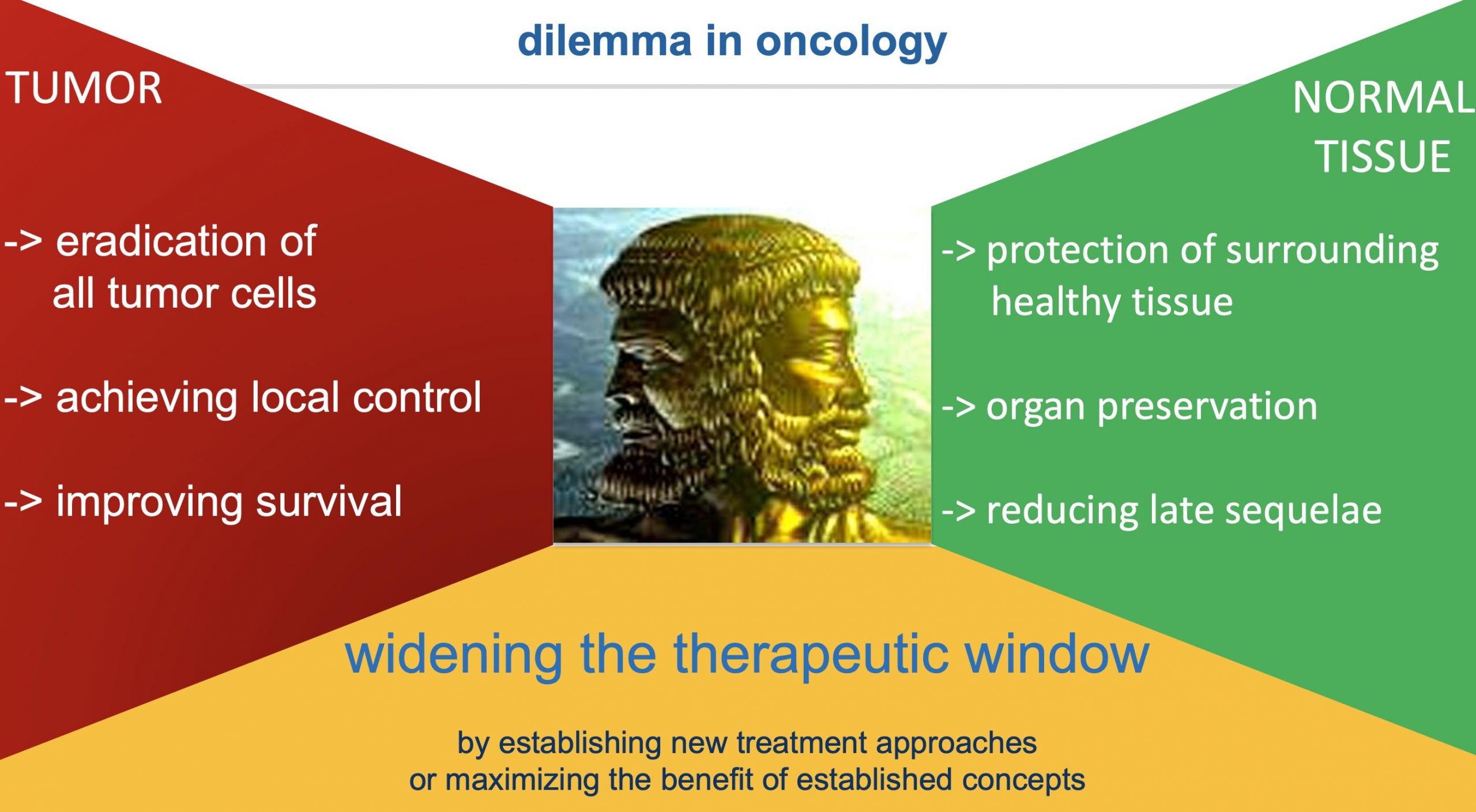
In the presentation titled “Central Nervous System Tumours” by Dr. Semi Harrabi from the Heidelberg Ion Beam Therapy Center at the University Hospital Heidelberg, Department of Radiation Oncology, key aspects of oncological dilemmas and the effectiveness of hadron therapy for brain tumors were discussed. The focus was on the eradication of all tumor cells, achieving local control, and improving survival while simultaneously protecting surrounding healthy tissue, preserving organs, and reducing late sequelae. The presentation highlighted the importance of establishing new treatment approaches or maximizing the benefits of established concepts to widen the therapeutic window in cancer treatment.
Harrabi also discussed the specifics of dose distribution in proton-based therapy, a concept first proposed by Robert D. Wilson in 1946. This therapy is characterized by a narrow peak, low entrance dose, depth of penetration depending on proton energy, and minimal exit dose. The presentation delved into the quantification of dosimetric potential, emphasizing target volume coverage and the protection of organs at risk.
Clinical outcomes were another significant aspect of the presentation, with a focus on brain tumors of low to intermediate malignancy (CNS grade I and II). Harrabi also addressed the characteristics of radiation-induced brain injuries, underlining the clinical evidence that proton relative biological effectiveness (RBE) increases significantly with increasing linear energy transfer (LET). The presentation concluded with questions about the future of carbon ion therapy and its potential applications in treating central nervous system tumors.